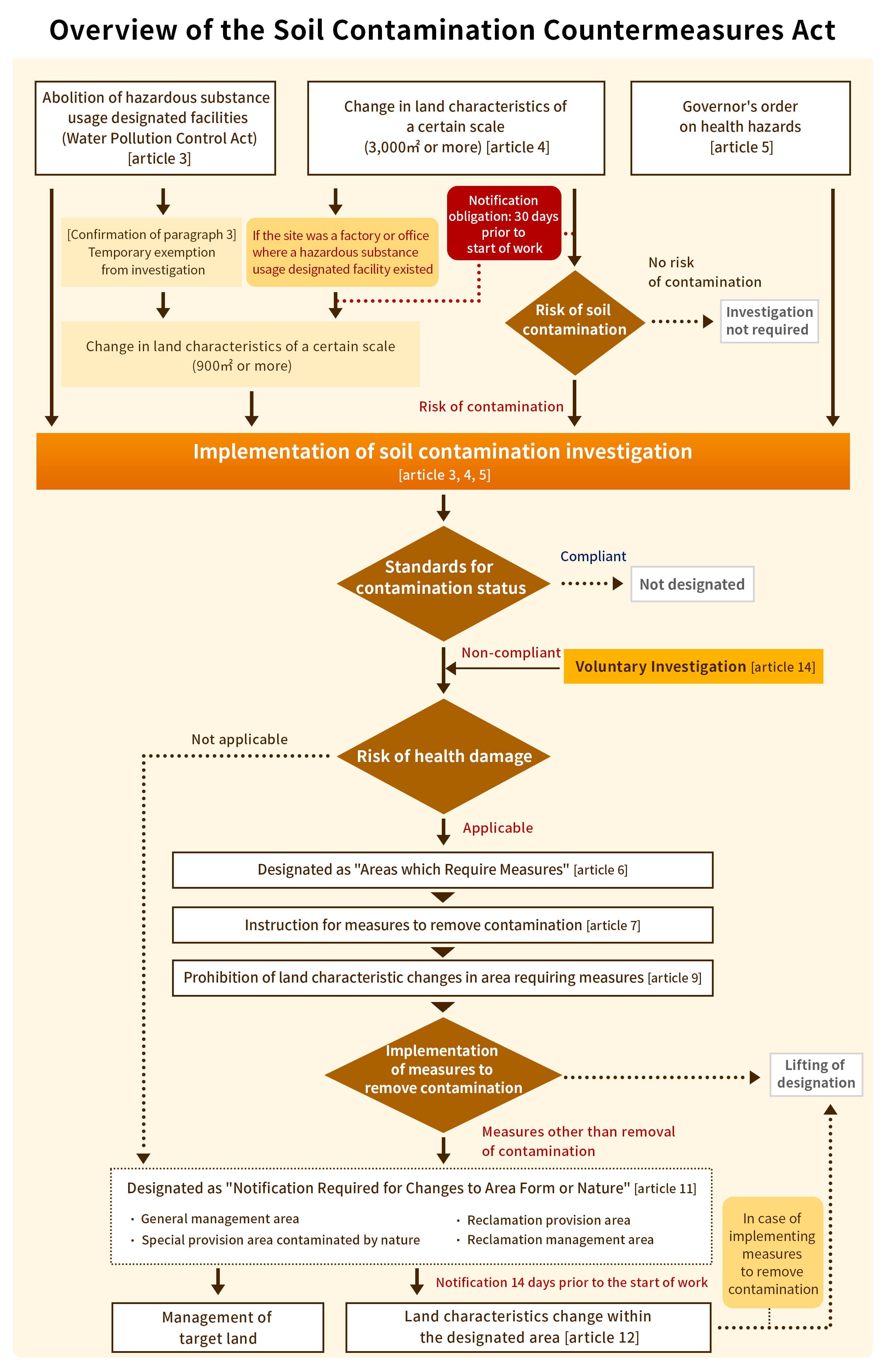
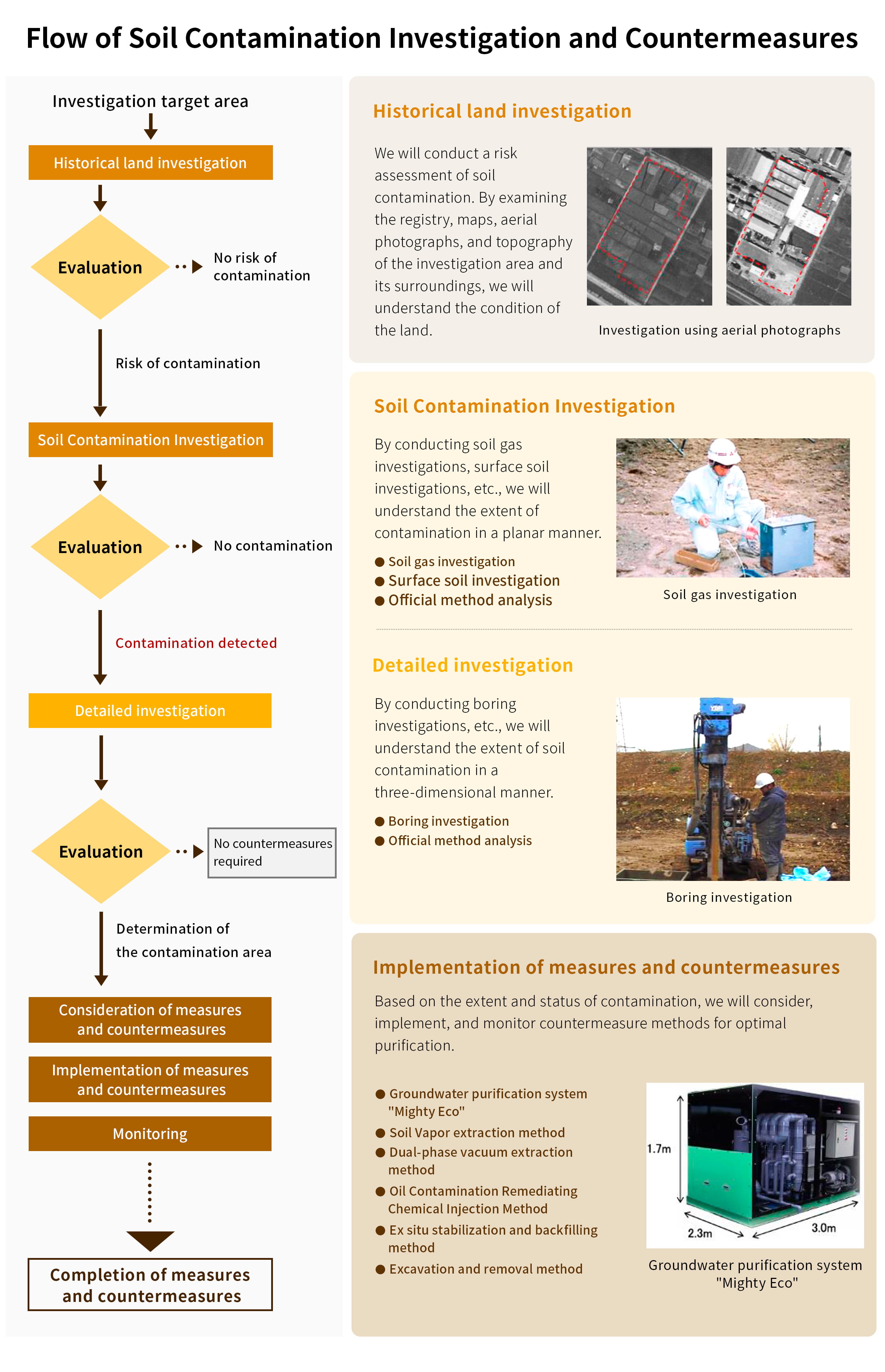
Soil Contamination Investigation and Countermeasures
Phase1 Environmental Site Assessment
Collect information of land use and history of designated hazardous substances use to assess the risk of soil contamination.
In Phase1 Environmental Site Assessment, information on current and histrical
land use in and around the target area from a variety of official, publicly available, and private records
are collected.
In addition to the information of a site visit to observe the current conditions, the environmental
professional interviews relevant parties to assess the risk of soil contamination.
Phase1 Environmental Site Assessment helps to narrow down the kinds of designated hazardous substances and
the extent of potential contamination at the site. The environmenatl professional uses the results to make
optimal soil contamination investigation plan.
Examples of Collected Data Items
| Classification | Official Documents | Public Documents | Private Documents | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Determining the scope of investigation area | Water Pollution Control Act, sewer notification records, investigation-order related documents | Certified copy of land registry, public map, urban planning map | Asset list and land survey map | |
| Changes in land use and ground surface elevation, geological information | Land use | City Planning Act, Act on Regulation of Residential Land Development | Copy of land registry, aerial photographs, residential area maps (previously obtained) | Factory guide, company history, building and facility layout plans |
|
Changes in ground surface elevation, geological information |
City Planning Act, Act on Regulation of Residential Land Development, Environmental Impact Assessment Act |
Topographic map (previously obtained), ground surface map, hydrogeological map |
Land development construction records, reclamation work record, geological survey reports, well drilling records |
|
|
Contamination status of hazardous substances |
Past documents on Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act |
Press releases, company environmental reports, CSR reports |
Past soil investigation and countermeasure reports (including voluntary investigations) |
|
| Information on the risk of contamination by specific hazardous substances | Burial of hazardous substances, etc. | Administrative procedure documents confirming the history of burial, scattering, leakage, or underground infiltration of specific hazardous substances | Press releases, company environmental reports, CSR reports | Records of hazardous substances burial, scattering, accidents, administrative guidance, complaints, disasters, etc. |
| Use of hazardous substances | Company history, city history, manufacturing method documents, patent information, etc. | List of handled substances, purpose, form, usage amount, usage location, usage period, facility structure, piping diagram, drainage route map, waste storage location, transportation route | ||
| Storage of hazardous substances, etc. | Company history, city history | List of substances, sds, waste records, transportation records, records of quantity / location / period / depth / piping | ||
| Others | Documents on considering contamination by nature, soil data of developed land, other documents | |||
| Information on reclamation of public water areas | Public Waters Reclamation Act (application for reclamation permit, application for change permit, application for completion permit, notification of start of reclamation work) | Certificate of All Records(property), aerial photographs (taken after march 15, 1977), Waste Management Act (notice of designation of reclamation site, register of designated areas), urban planning map | Land development construction records | |
Hearing Items (Examples)
| Information on past land use |
|
|---|---|
| Information on risk of contamination |
|
Phase2 Environmental Site Assessment
Phase2 Environmental Site Assessment is soil contamination investigations that collects samples and analyzes to understand the area and concentration of contamination.
When the presence of any hazardous substances is identified by Phase1
environmental Site Assessment, samples of soil vapor and surface soil are collected.
We can provide consistent support from sampling, analysis, and report submission.
If the analysis results of the surface samples exceed standard values, a boring investigation is conducted
to determine the depth of contamination and the presence of groundwater contamination to accurately assess
the situation.
Soil and Groundwater Contamination Countermeasures
Pump & Treat Method
Mighty Eco is a volatile organic compound removal system developed by combining
our long-accumulated knowledge in anti-pollution measures with the jetting and agitation technology of the
YBM Corporation, a manufacturer of environmental equipment, including low-noise soil survey equipment.
This method performed strongly and with ease in the demonstration test, "Development and Dissemination
Survey
on General Purification Equipment for Groundwater Pollution" conducted by the Ministry of the Environment in
2001.

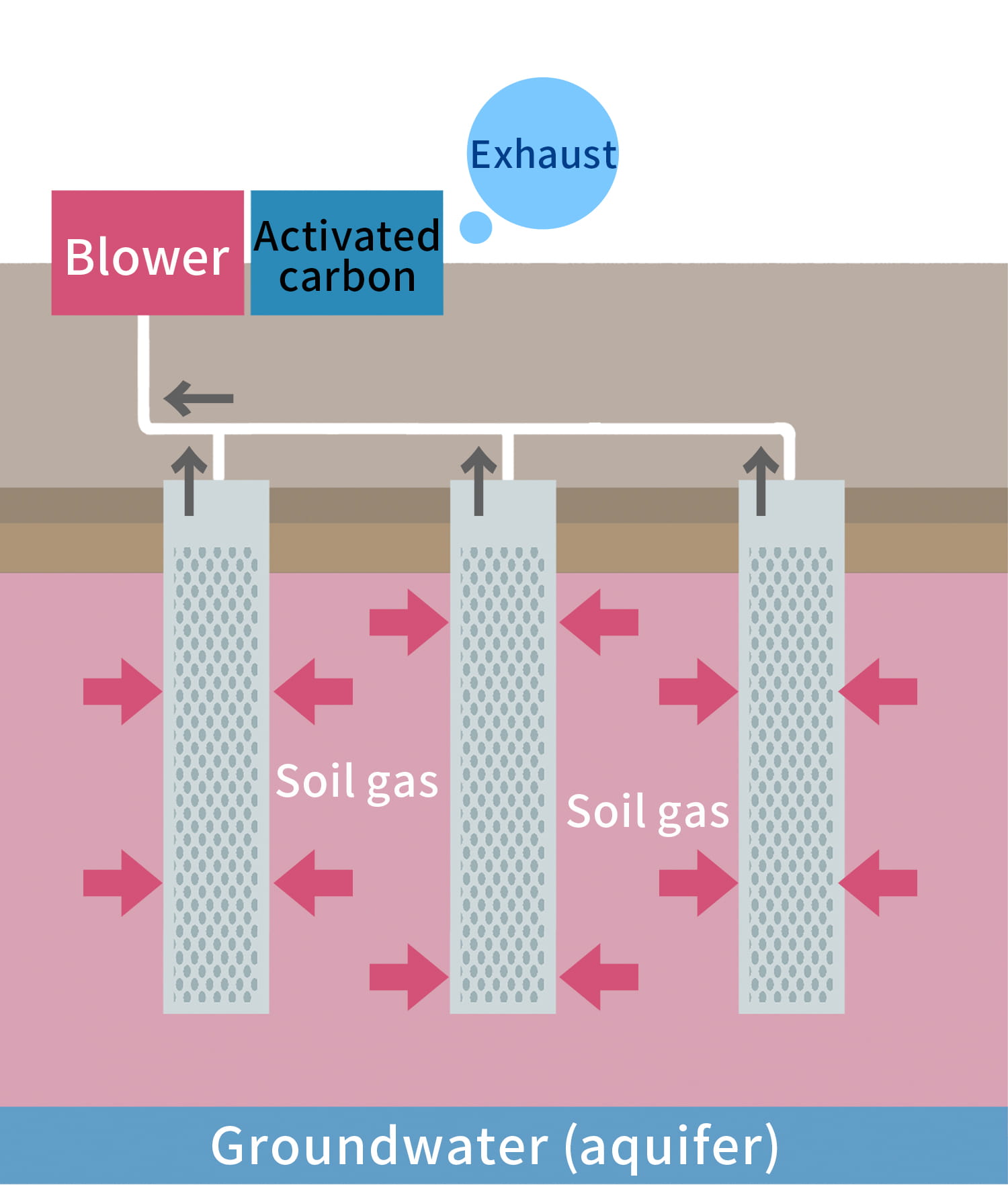
Soil Vapor Extraction Method
Volatile organic compounds volatilized in the pore spaces of soil particles are
vacuumed and removed as soil vapor.
The suctioned air is absorbed in an activated carbon adsorption tower installed on the ground, and the clean
air is released into the atmosphere.

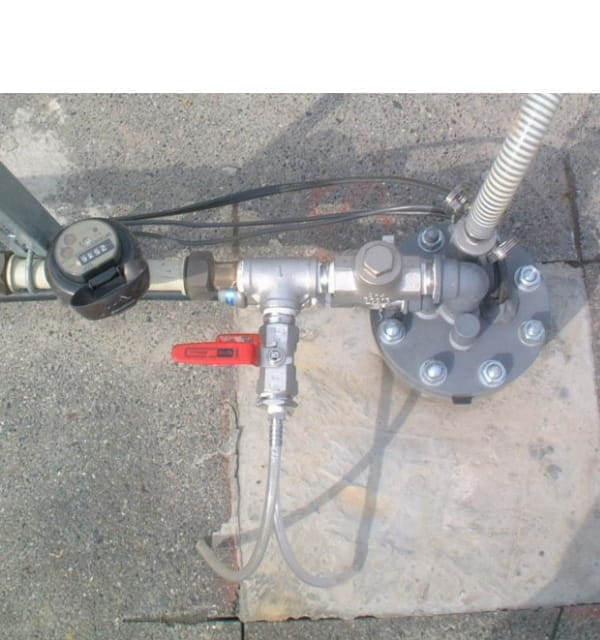
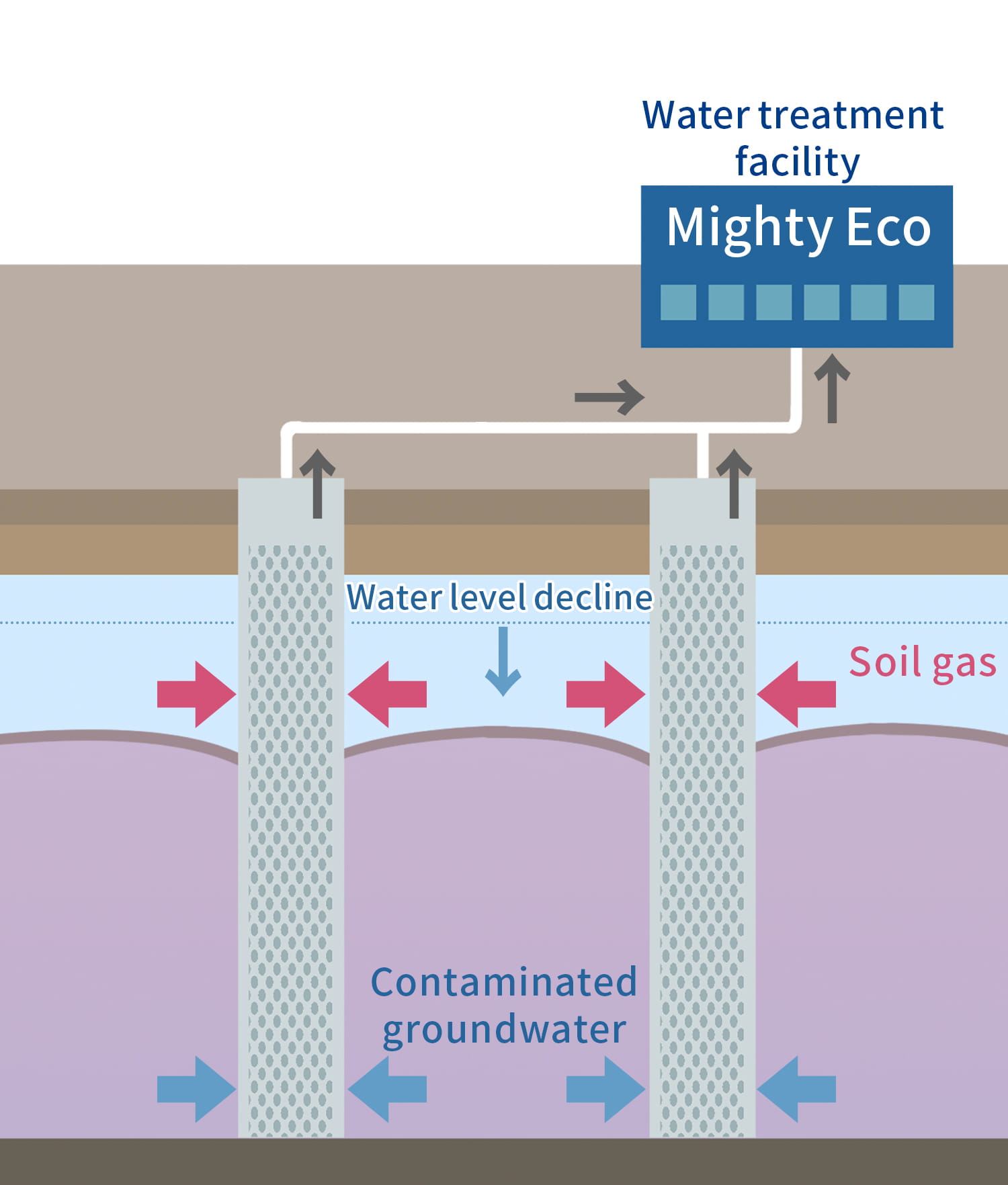
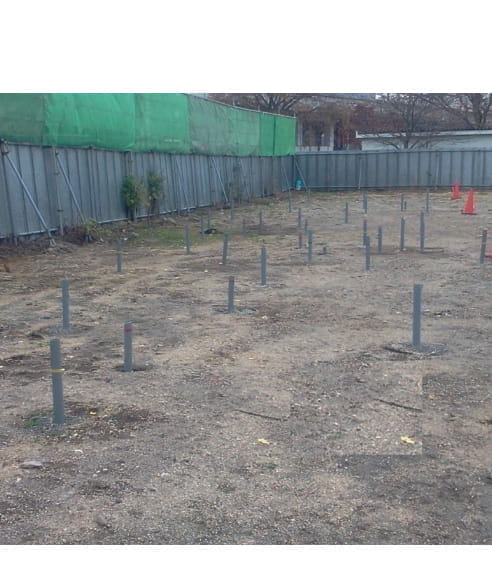
Dual-phase vacuum extraction Method
Dual-phase vacuum extraction is the efficient remediation system of high concentration of contamination by the combination of Pump & Treat system and Soil Vapor Extraction system.

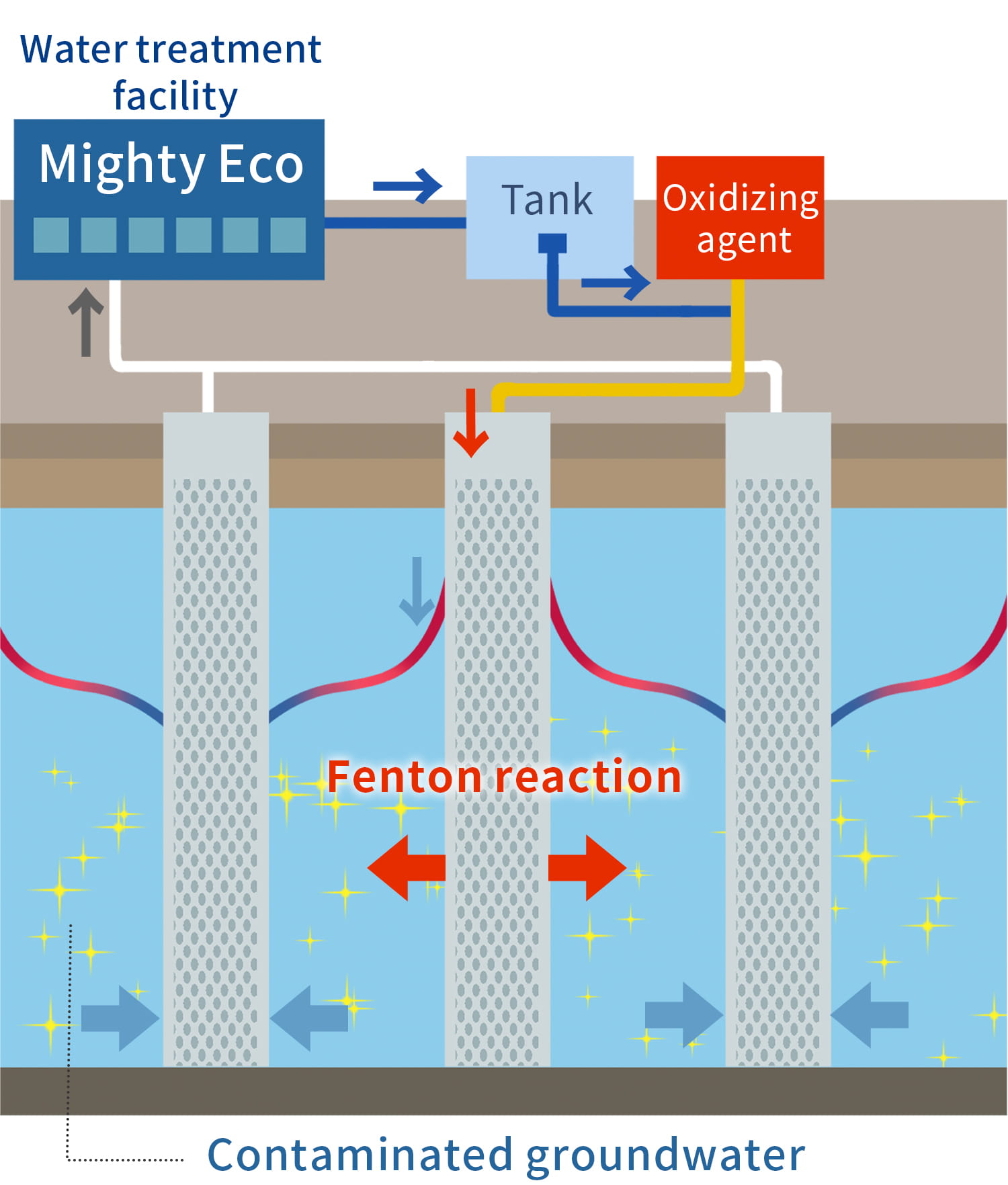
Oxidative Decomposition Method (Circulation Method with Oxidant)
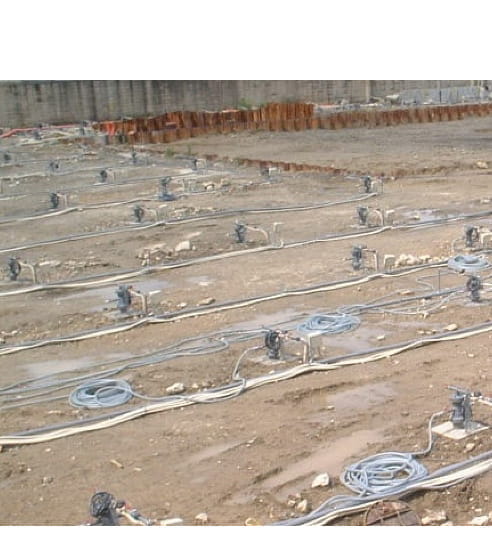
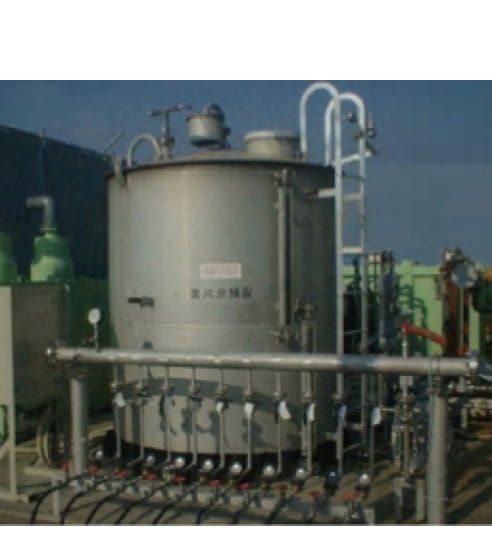
This is a method to decompose and detoxify volatile organic compounds in geological layers by injecting an oxidant into pumped-up groundwater and circulating it. This method was selected for "FY2003 Soil Investigation and Countermeasure Technique for the Soil Contaminated with Designated Hazardous Substance, which is Low-cost and has Low Environmental Burden" by the Ministry of the Environment and was rated highly in the demonstration test conducted by Yamagata Prefecture, as shown on their website.


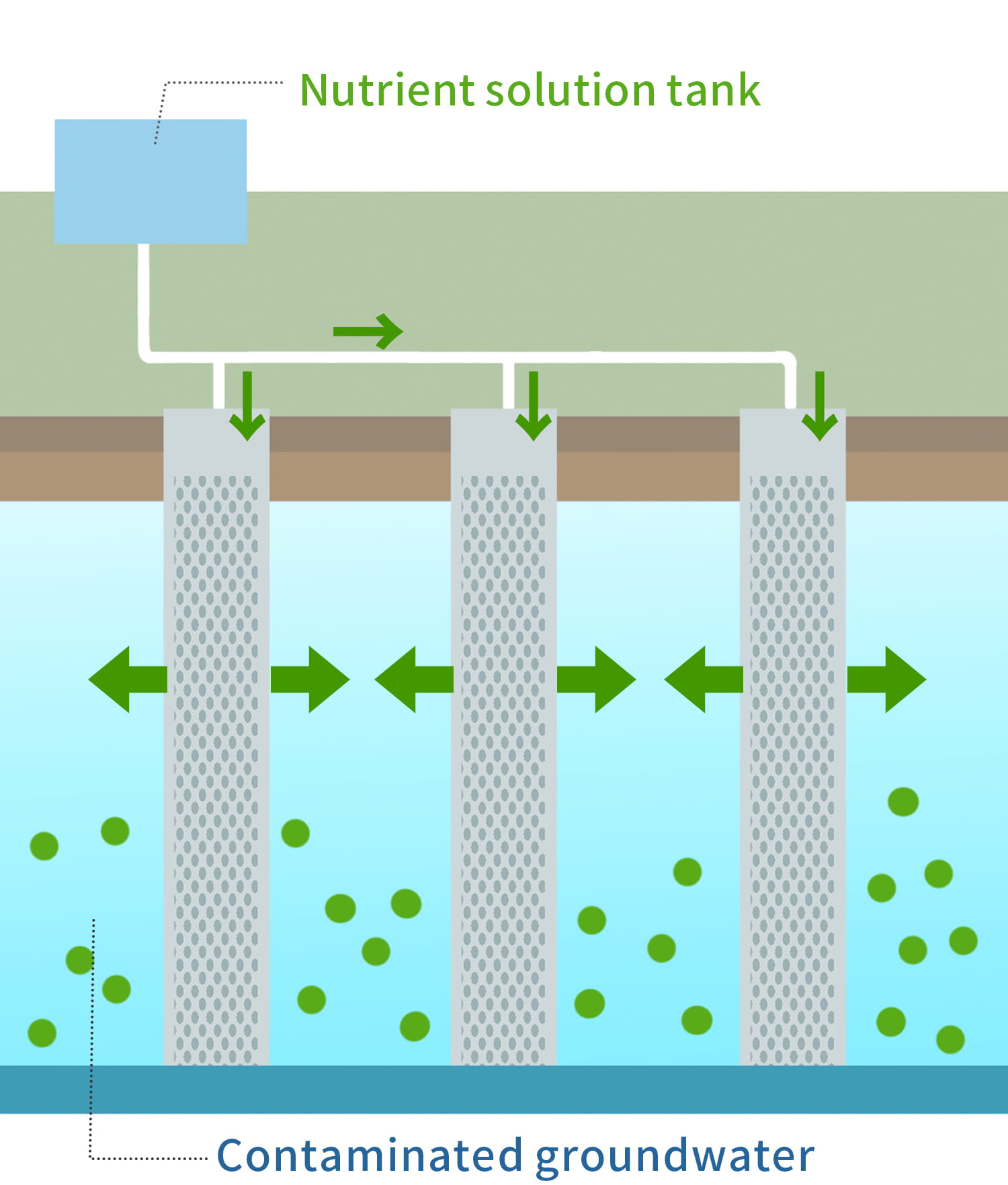
Bioremediation Method
This method uses nutritional supplements to activate indigenous microorganisms and detoxifies volatile organic compounds, hexavalent chromium, oil, etc. through biological degradation. The nutritional supplements to be injected are safe because they derive from food and are degradable.
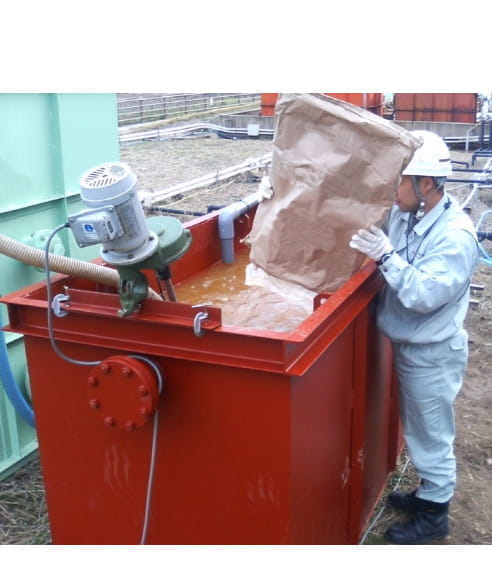


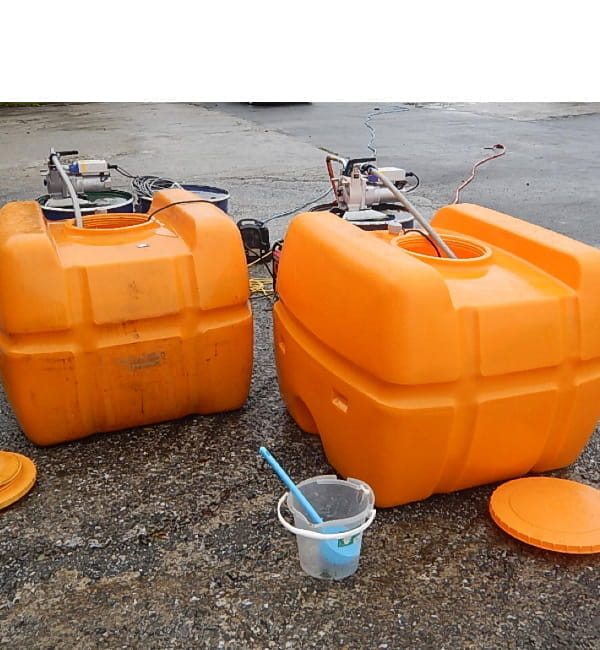
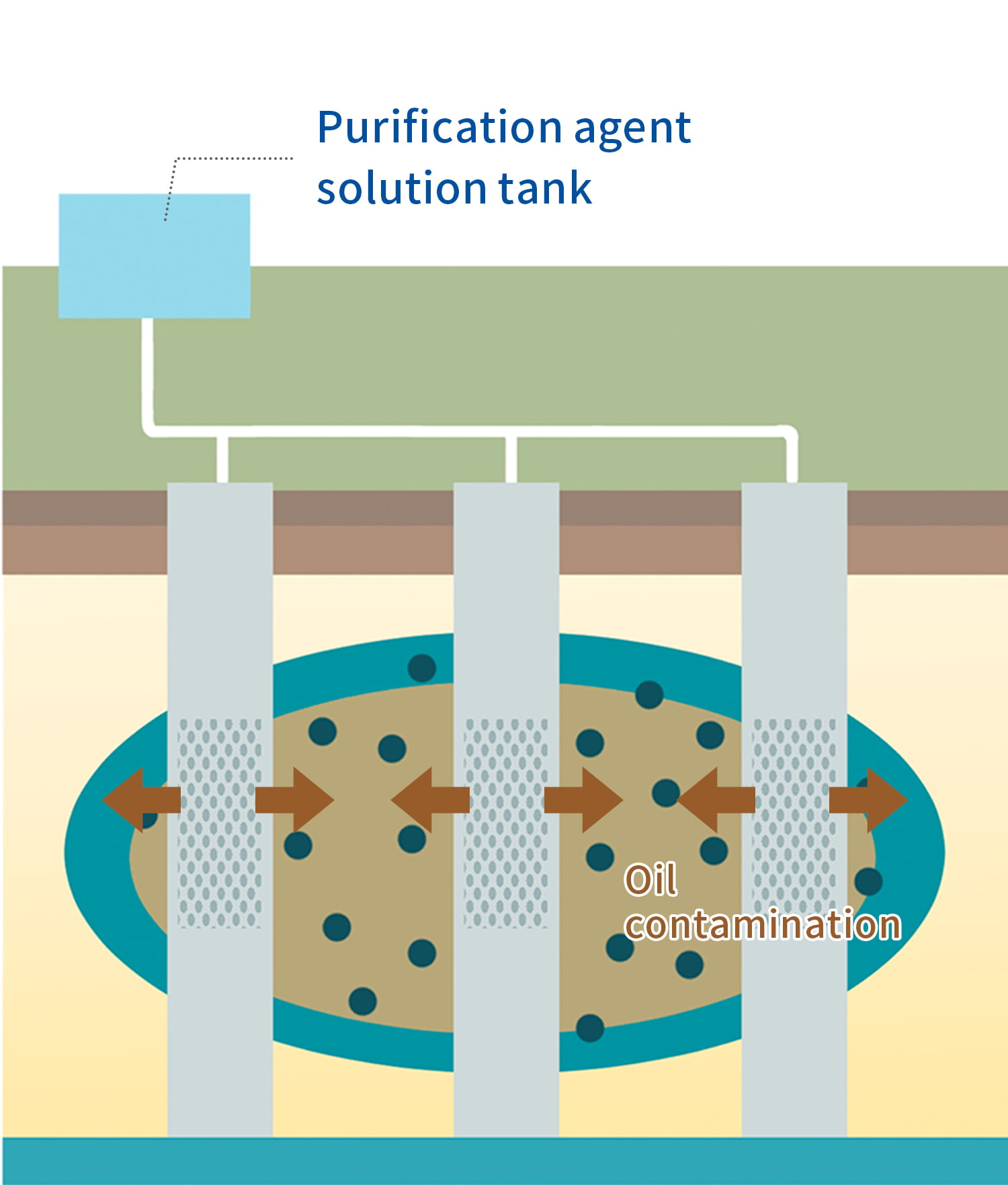
Oil Contamination Remediating Chemical Injection Method
In addition to "oil-degrading bacteria" and "nutritional supplements," hand-picked "thickening agents" will be injected into the soil and biologically degrade the oil. By injecting thickening agents, remediating chemicals will be less likely to diffuse in the groundwater and more likely to stay in the contaminated area, resulting in faster oil degradation.
Patent Pending (regarding thickening agents)
Co-developers: Mitsubishi Materials Techno Corporation, GATE Co, Ltd., Prefectural University of Hiroshima

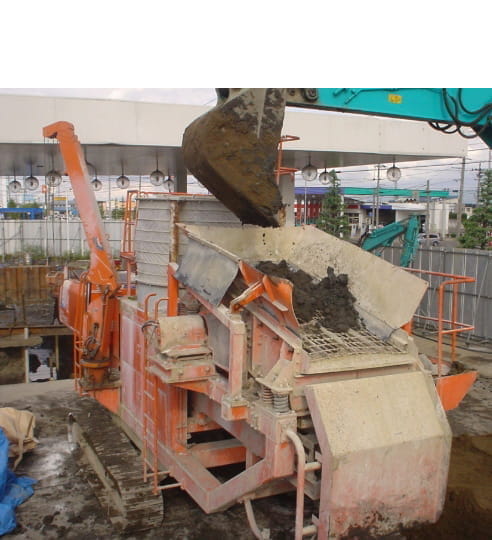
Ex Situ Stabilization and Backfilling Method
This is a method to prevent the diffusion and transfer of contaminants to the
surrounding areas by adding and mixing insolubilizing agents to the soil with heavy metal contamination to
make the hazardous materials harder to dissolve.
This method is effective for soil that does not meet the second elution standards of the Soil Contamination
Countermeasures Act when the contaminated soil is to be contained or carried to an off-site disposal
location.
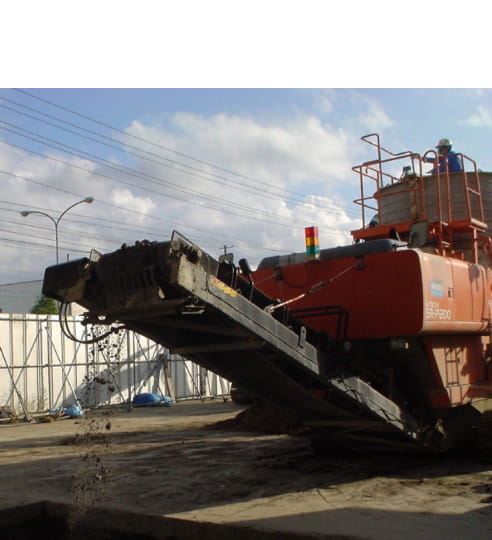
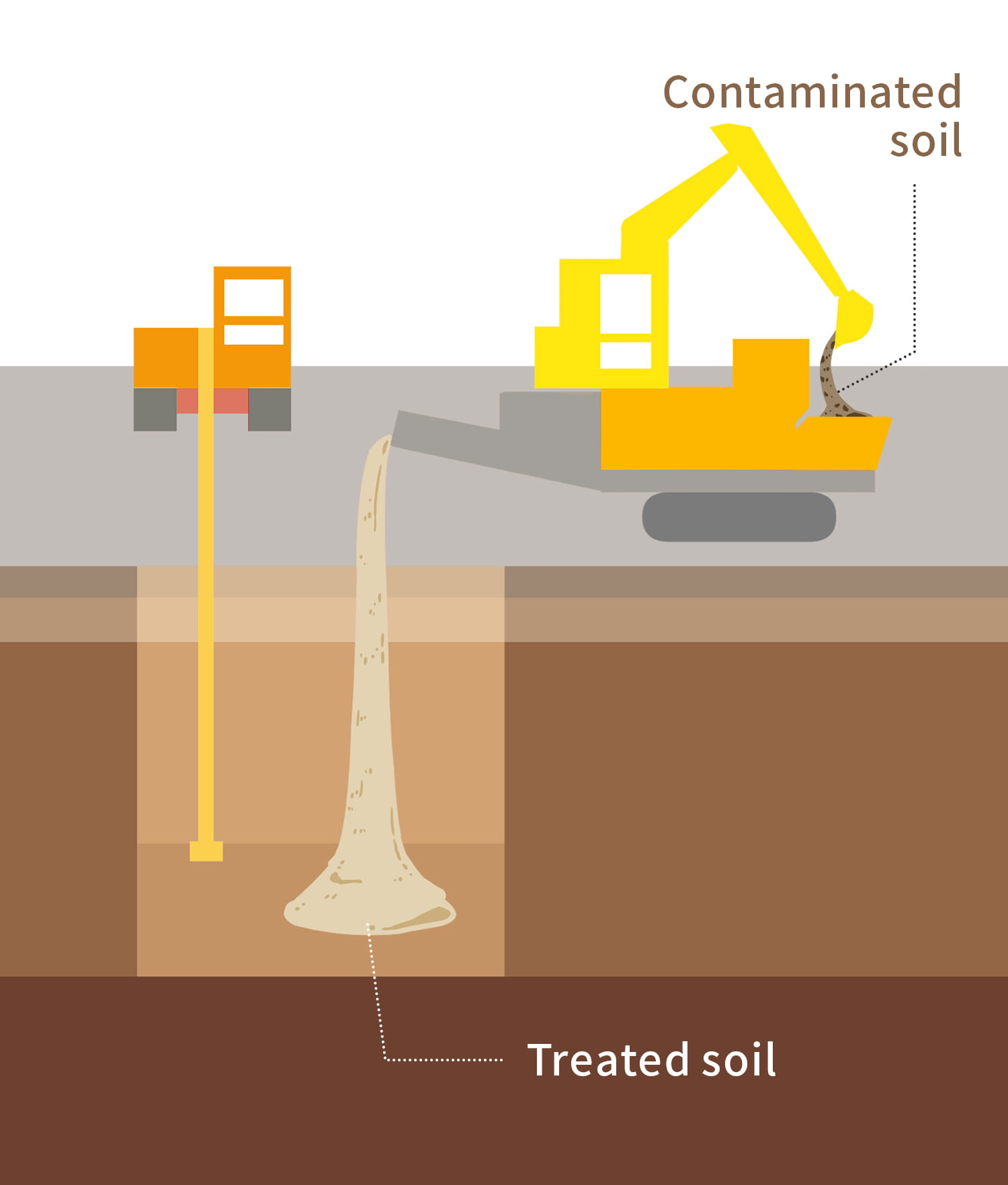


Excavation and Removal Method
This method is to dig the contamination area and carry it off-site.
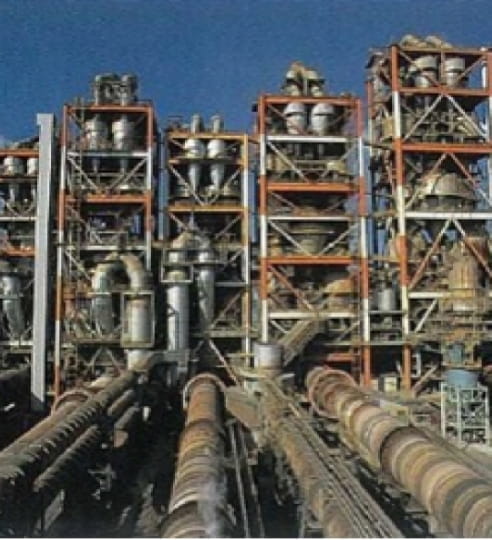
We can dispose of the contaminated soil at locations across Japan using the network of our group company,
Mitsubishi UBE Cement Corporation.
* The picture on the right is their Kyushu plant, which has the largest production capacity in Japan.
(Kanda-machi, Miyako-gun, Fukuoka)
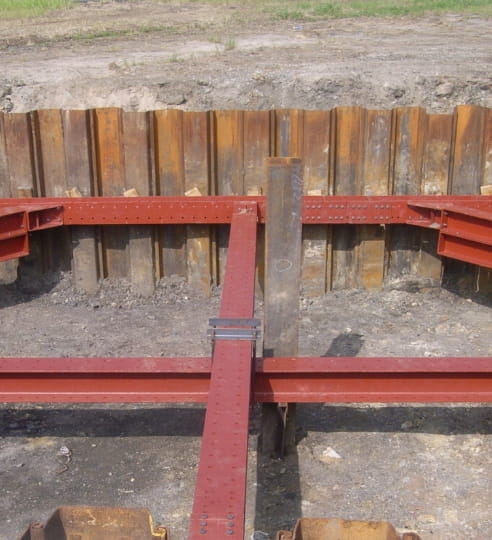
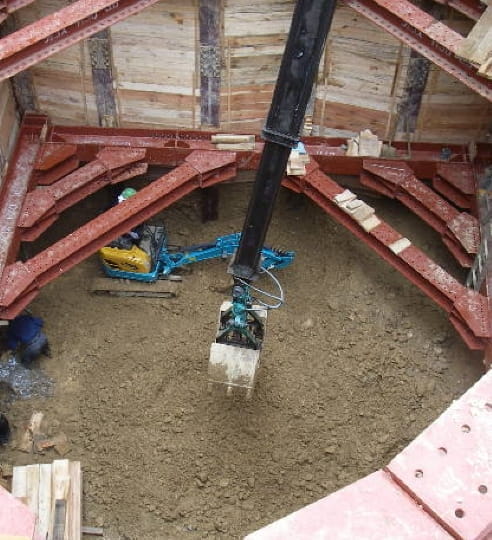



Use of multiple remediation methods
We can propose plans with a combination of remediation methods to efficiently remediate contamination.
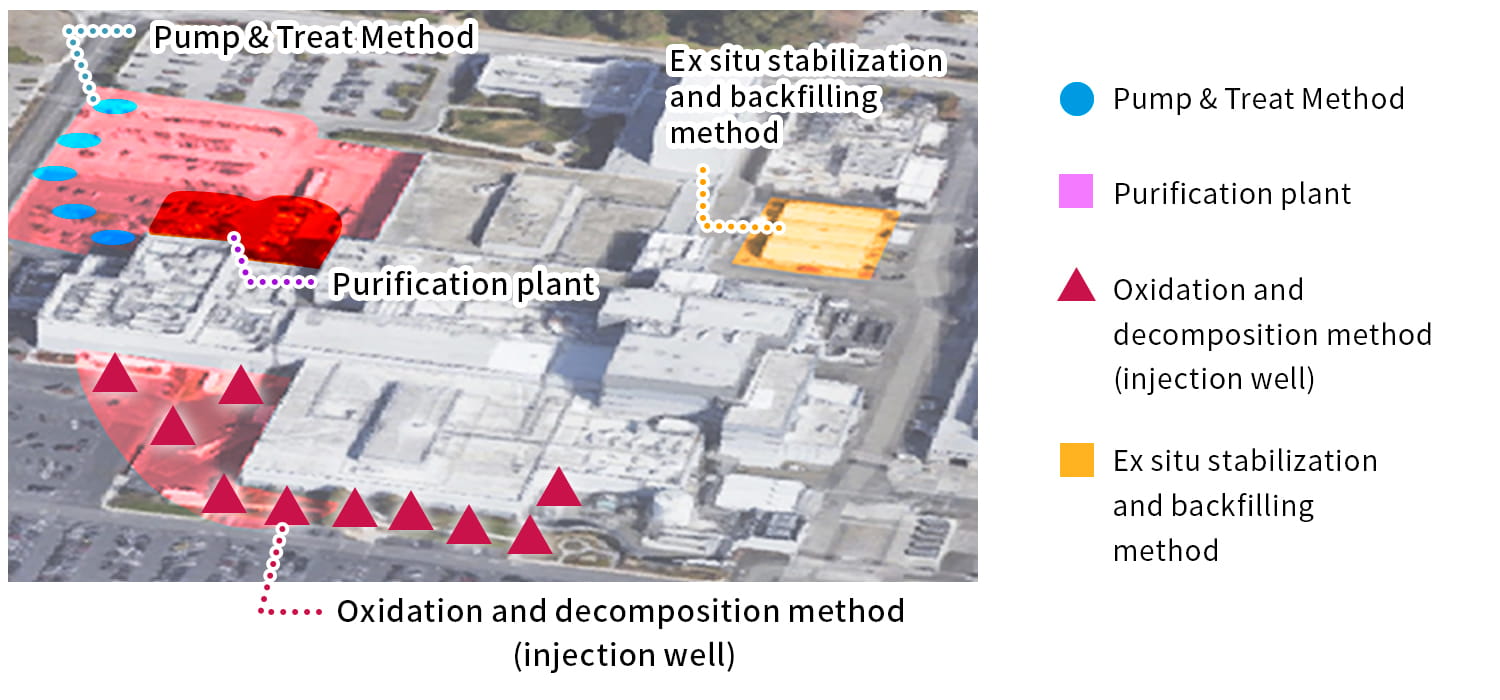
We propose different methods, such as remediation of a contaminated area, disposal of contaminated soil, etc., to meet clients' needs.
We propose abundant countermeasure technologies depending on the contamination situation (e.g. contamination concentration and whether there is contamination in groundwater) and the client's construction plan.
- A technology to remediate soil by drilling a well and injecting chemical agents underground without removing soil.
- A technology to remediate soil by removing soil or injecting chemical agents into excavated soil and reburying it.
Complying with the guideline of the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act, we can conduct the methods mentioned above to prevent the spread of contamination and remediate soil.